C5: Environmental Impact
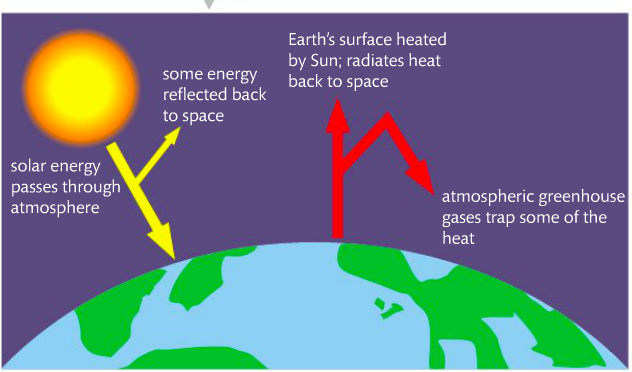
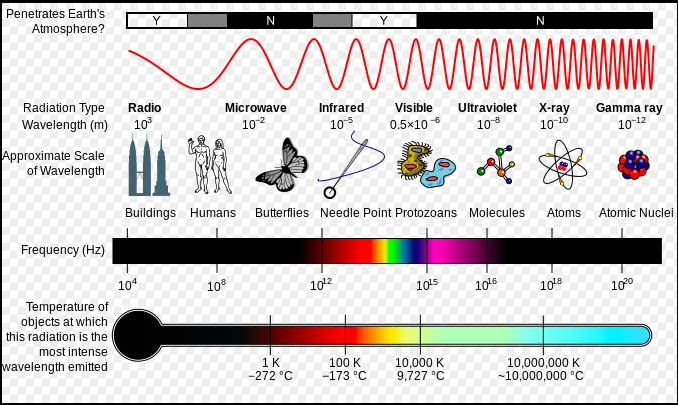
Evidence exists that increased levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere produced by human activities are changing the climate. This upsets the balance between radiation entering and exiting the atmosphere that leads to climate change. Sunlight has a range of wavelengths (see p. 680 in your text). The highest frequencies are absorbed by the upper atmosphere, allowing some UV, visible and longer wavelengths to reach the surface where they are absorbed. The waves re-emitted from the surface are longer wavelength infrared. These waves interact with carbon dioxide, methane and water vapor (the main greenhouse gases) which capture this energy so that it remains trapped in Earth's atmosphere.
The IR radiation interacts with the covalent bonds of greenhouse gas molecules, causing them to bend and stretch. The IR radiation causes the molecules to vibrate, achieving resonance. The C-H, C=O, and O-H bonds in greenhouse gases have resonant frequencies of vibration in the IR region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Image courtesy of Wikipedia.
Carbon dioxide emissions have increased dramatically since the industrial revolution. Page 682 in your text shows the average CO2 increases for the 20th century and the global land-temperature index.
The main sources of greenhouse gas emissions are: burning fossil fuels (which accounts for 50% of anthropogenic greenhouse gases), industrial gases from factories that produce not only CO2, but also nitrogen oxides (which account for 25% of human greenhouse gas production, and agriculture/deforestation (the remaining 25%).
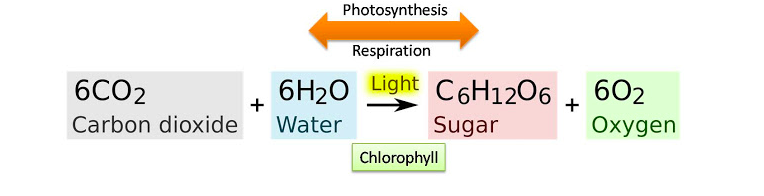
Burning fossil fuels release the carbon dioxide that comes from hydrocarbons previously stored underground. Industrial gases introduce not only CO2 but also other gases, such as chlorofluorocarbons (which do not occur naturally). Agriculture increases methane concentration from farty animals such as sheep and cows who generate methane in their digestive systems. Deforestation increases CO2 because with fewer trees, less carbon dioxide is absorbed from the atmosphere and used in photosynthesis.
Page 684 breaks down the chemistry that occurs between CO2 gas and aqueous CO2 occurring at the ocean's surface. CO2 itself is not very soluble. The overall process produces a small positive delta H, which increases the temperature and shifts equilibrium to the left and lowers the ability of CO2 to dissolve in water.
Methane and nitrous oxide are the main greenhouse gases produced in agriculture. Methane is 25X as powerful a greenhouse gas as CO2 while nitrous oxide has over 300X the impact. Changing from nitrogen-based fertilizers to crop rotation methods could increase the levels of CCS and reduce emissions. The use of urban space to grow crops could subsidize local communities and reduce transport costs.
Smoke, dust particles and clouds reflect sunlight back into space, causing global dimming which cools the Earth's surface. Soot and ash can change the properties of clouds, polluting them and causing them to reflect more light than normal clouds. Global dimming has harmful effects: causing acid rain, decreased evaporation rate for water, and health problems such as asthma.









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed