Housekeeping: We will finish up Chapter 1 this week. Your exam over Ch 1 is scheduled for November 24th. Your LR lab (final) is due November 30th. Other than that, unless y'all know something I don't, our house is clean.
Agenda:
1. Solution Stoichiometry
2. Gas Laws
Content Review:
Textbook Readings: Section 1.3
Student Missions:
Mission 1: The Problem is the Solution!
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Describe the components of a solution
2. Calculate concentration of a solution using the c = n/V equation and c1V1=c2V2 equation.
Section 1.3: Solutions gives you an overview of solution chemistry. Terms to know: solute, solvent, concentration, dilute, stock solution, volumetric analysis and titration.
Molar concentration of a solution is defined as the amount in moles of a substance dissolved in 1L (1 dm-3) of a solvent (usually water). The formula for concentration is on page 31 of your textbook.
Agenda:
1. Solution Stoichiometry
2. Gas Laws
Content Review:
Textbook Readings: Section 1.3
Student Missions:
Mission 1: The Problem is the Solution!
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Describe the components of a solution
2. Calculate concentration of a solution using the c = n/V equation and c1V1=c2V2 equation.
Section 1.3: Solutions gives you an overview of solution chemistry. Terms to know: solute, solvent, concentration, dilute, stock solution, volumetric analysis and titration.
Molar concentration of a solution is defined as the amount in moles of a substance dissolved in 1L (1 dm-3) of a solvent (usually water). The formula for concentration is on page 31 of your textbook.
Doc Brown's chemistry page has a nice summary regarding concentration. Remember, however, that the term "molarity" is falling out of use, and instead "c" for concentration should be used in its place. You should go through the practice problems which include the solutions (get it?).
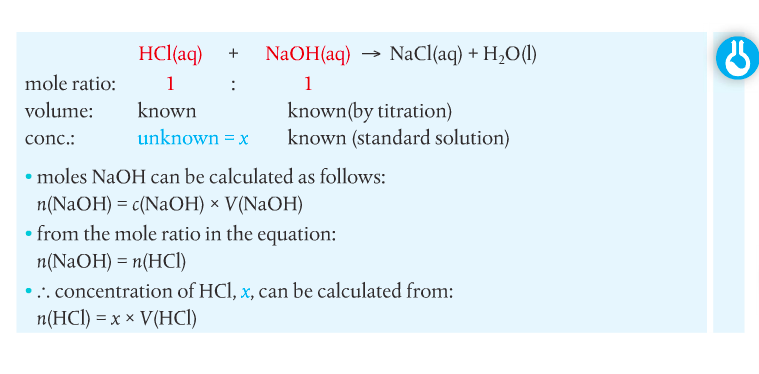
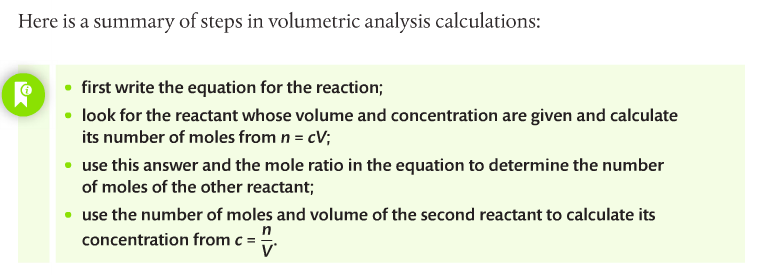
You have to complete a titration practical. Quantitative analysis includes a range of techniques to determine the amount or concentration of an analyte. An analyte is the substance under analysis.
Volumetric analysis is a quantitative technique used by chemists involving two solutions. A titration involves a standard solution of known concentration which is added to a solution of unknown concentration until the reaction is complete. The reaction progress is monitored through color changes using indicators.
You have to complete a titration practical. Quantitative analysis includes a range of techniques to determine the amount or concentration of an analyte. An analyte is the substance under analysis.
Volumetric analysis is a quantitative technique used by chemists involving two solutions. A titration involves a standard solution of known concentration which is added to a solution of unknown concentration until the reaction is complete. The reaction progress is monitored through color changes using indicators.
Homework. Solutions are included so you can check your work.
Concentration Dilution Solution Preparation
Concentration Dilution Solution Preparation
Mission 2: The Gas Laws
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Explain the Kinetic Theory of Gases.
2. Describe conditions at STP.
3. Complete calculations using gas laws.
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Explain the Kinetic Theory of Gases.
2. Describe conditions at STP.
3. Complete calculations using gas laws.
You can check your work below.
| chapter1_answers.pdf |

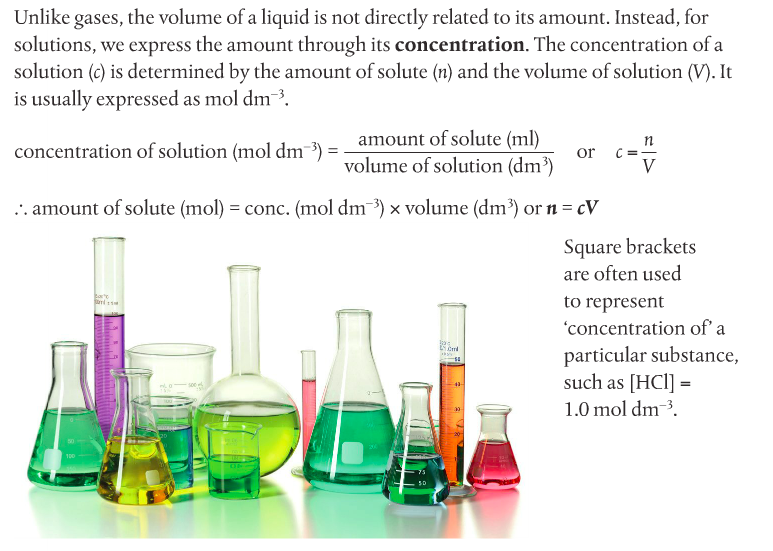


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed