Housekeeping: Welcome to the Mad!Lab!
There is a lot of drawing in this course. You are expected to keep an art kit (pencils, pens, erasers, markers, etc) in your bags so that you can sketch when the lesson calls for it.
Agenda:
Welcome
Introduction to the course
Class procedures
Content Review:
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
Sections 2.1, 2.2 & 2.3
Macromolecules
Student Missions:
Mission 1: Breaking It All Down.
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
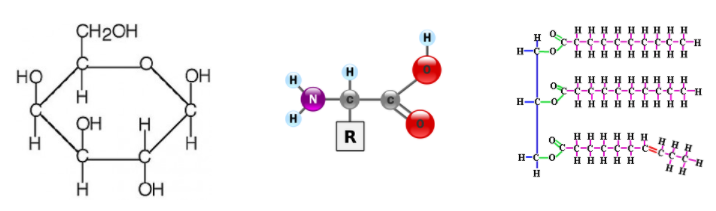
1. Draw molecular diagrams of glucose, ribose, a saturated fatty acid and a general amino acid.
2. Describe metabolism in terms of its component processes.
3. Explain the difference between condensation and hydrolysis reactions.
4. Identify biomolecules such as sugars, lipids and amino acids based on their structures.
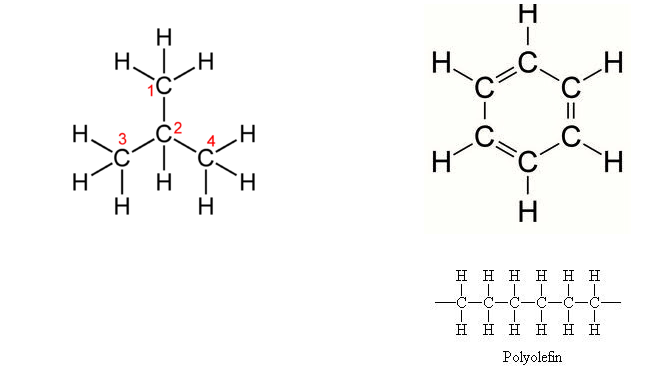
Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds, which allows a diversity of stable compounds to exist. As a result, carbon-containing organic molecules can form chains, rings, and branched chains.
There is a lot of drawing in this course. You are expected to keep an art kit (pencils, pens, erasers, markers, etc) in your bags so that you can sketch when the lesson calls for it.
Agenda:
Welcome
Introduction to the course
Class procedures
Content Review:
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
Sections 2.1, 2.2 & 2.3
Macromolecules
Student Missions:
Mission 1: Breaking It All Down.
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Draw molecular diagrams of glucose, ribose, a saturated fatty acid and a general amino acid.
2. Describe metabolism in terms of its component processes.
3. Explain the difference between condensation and hydrolysis reactions.
4. Identify biomolecules such as sugars, lipids and amino acids based on their structures.
Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds, which allows a diversity of stable compounds to exist. As a result, carbon-containing organic molecules can form chains, rings, and branched chains.
These different structures allow for the creation of macromolecules. Macromolecules are, quite obviously, large molecules. There are four kinds: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each macromolecule has its own building blocks. Carbohydrates are composed of monosaccharides (simple sugars), proteins are composed of amino acids, lipids are composed of glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphate groups, and nucleic acids are formed from nucleotides.
Let's go here and talk about metabolism and catabolism. What happens when we eat?
Homework: In this PowerPoint, complete Tasks #1, 2 and 3. This is your first assignment.
Mission 2: Well, It's What We're Made Of, Right?
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Compare the thermal properties of water with those of methane.
2. List and describe the essential properties of water.
3. Explain the necessity of hydrogen bonding.
4. Explain the solubility of water and its relationship to transporting molecules in organisms.
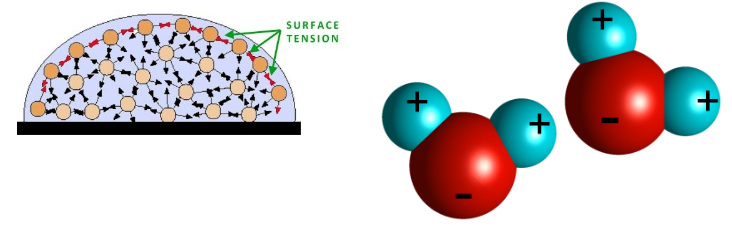
Water is the medium of life. Understanding why it is so important requires understanding of its structure. There are two hydrogen ions sharing electrons with an oxygen ion. Sharing of electrons results in a covalent bond. The water molecule is polar, meaning that it has a net charge on one end (the oxygen end). As a result, water can interact with itself and other molecules in different ways. Water has many different properties which makes it so important in living organisms.
Homework: In this PowerPoint, complete Tasks #1, 2 and 3. This is your first assignment.
Mission 2: Well, It's What We're Made Of, Right?
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Compare the thermal properties of water with those of methane.
2. List and describe the essential properties of water.
3. Explain the necessity of hydrogen bonding.
4. Explain the solubility of water and its relationship to transporting molecules in organisms.
Water is the medium of life. Understanding why it is so important requires understanding of its structure. There are two hydrogen ions sharing electrons with an oxygen ion. Sharing of electrons results in a covalent bond. The water molecule is polar, meaning that it has a net charge on one end (the oxygen end). As a result, water can interact with itself and other molecules in different ways. Water has many different properties which makes it so important in living organisms.
Let's go here and talk more about why water's so freakin' awesome.
Homework: Complete Tasks #4, 5 and 6 in the PowerPoint.
Mission 3: Carbohydrates & Lipids
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Describe the structures of saccharides and provide examples.
2. Explain the differences between saturated and unsaturated fats.
3. Apply the structure of a triglyceride to its role in the human diet.
Let's go here.
Homework: Complete Tasks #4, 5 and 6 in the PowerPoint.
Mission 3: Carbohydrates & Lipids
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Describe the structures of saccharides and provide examples.
2. Explain the differences between saturated and unsaturated fats.
3. Apply the structure of a triglyceride to its role in the human diet.
Let's go here.
G11 Bio Review questions; Sections 2.1, 2.2 & 2.3.
Outline condensation and hydrolysis reactions using a different example for each.
Outline the effect of temperature and substrate concentration on the activity of enzymes.
Outline the role of hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Explain the importance of enzymes to human digestion.
State four elements that are needed by living organisms, other than carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, giving one role of each.
Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage.
Explain how the properties of water are significant to living organisms.
Outline condensation and hydrolysis reactions using a different example for each.
Outline the effect of temperature and substrate concentration on the activity of enzymes.
Outline the role of hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Explain the importance of enzymes to human digestion.
State four elements that are needed by living organisms, other than carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, giving one role of each.
Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage.
Explain how the properties of water are significant to living organisms.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed