Kinetics
Complete the tasks found here. You will need to reference this page in order to complete all the questions.
Mission 1: Reaction Mechanisms.
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Define "kinetics" and "reaction mechanism."
2. Explain the factors that affect rates of reaction.
3. Describe kinetic theory in terms of the movement of particles whose average KE is proportional to temperature in kelvin.
4. Investigate rates of reaction experimentally and evaluate the results.
5. Identify different techniques used to measure reaction rates.
The mechanism of a chemical reaction is the series of events that takes place as reactants are converted into products. You can read more about it on ChemWiki.
Mission 1: Reaction Mechanisms.
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Define "kinetics" and "reaction mechanism."
2. Explain the factors that affect rates of reaction.
3. Describe kinetic theory in terms of the movement of particles whose average KE is proportional to temperature in kelvin.
4. Investigate rates of reaction experimentally and evaluate the results.
5. Identify different techniques used to measure reaction rates.
The mechanism of a chemical reaction is the series of events that takes place as reactants are converted into products. You can read more about it on ChemWiki.
Go HERE to learn more about the factors that affect reaction rates.
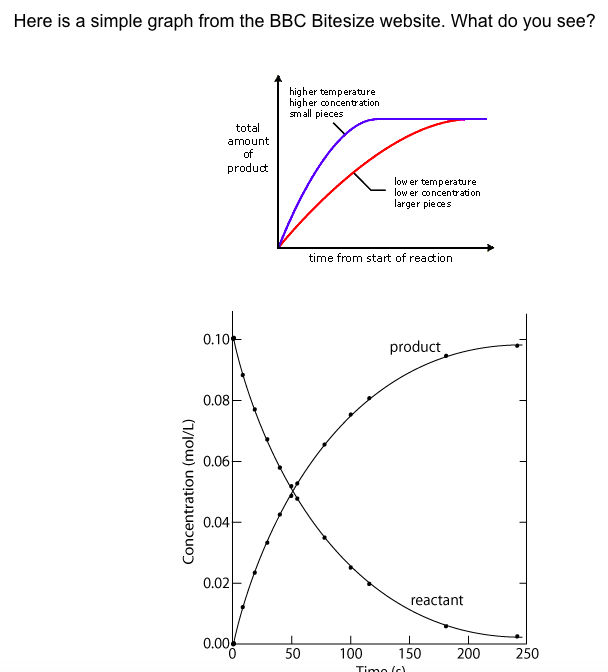
Collision Theory. Particles in a substance move randomly as a result of the kinetic energy that they possess. A convenient way to describe the kinetic energy ofd a substance is to take the average of the range of values of the particles in the substance. To do this, you take the temperature of the sample, measured in Kelvin. When a substance is supplied with extra energy via heat, the average kinetic energy of the particles increases and the temperature increases as well.
In order for reactions to take place, particles must collide (1) with enough energy, (2) in the correct orientation. Think back to the energy curves we investigated last spring. The energy required for a reaction to take place is called activation energy (Ea). Adding a catalyst lowers Ea and causes reactions to go faster. Particles have to be oriented in the correct geometry when they collide in order for a product to form. If the particles collide incorrectly, the reaction does not take place.
Want to learn more about reaction rates and different techniques? BBC Bitesize has you covered.
Collision Theory. Particles in a substance move randomly as a result of the kinetic energy that they possess. A convenient way to describe the kinetic energy ofd a substance is to take the average of the range of values of the particles in the substance. To do this, you take the temperature of the sample, measured in Kelvin. When a substance is supplied with extra energy via heat, the average kinetic energy of the particles increases and the temperature increases as well.
In order for reactions to take place, particles must collide (1) with enough energy, (2) in the correct orientation. Think back to the energy curves we investigated last spring. The energy required for a reaction to take place is called activation energy (Ea). Adding a catalyst lowers Ea and causes reactions to go faster. Particles have to be oriented in the correct geometry when they collide in order for a product to form. If the particles collide incorrectly, the reaction does not take place.
Want to learn more about reaction rates and different techniques? BBC Bitesize has you covered.
Mission 2: Dem Graphs Again!!!
Mission Objective. You should be able to...
1. Sketch and explain energy profiles with and without catalysts.
Mission Objective. You should be able to...
1. Sketch and explain energy profiles with and without catalysts.
The point of Mission 2 is for you to be able to read and interpret different rate graphs and provide a reasonable explanation as to what is going on, so make sure you pay close attention to the graphs in your text.
Mission 3: Dudes Named Max and Bolt (sort of)...
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
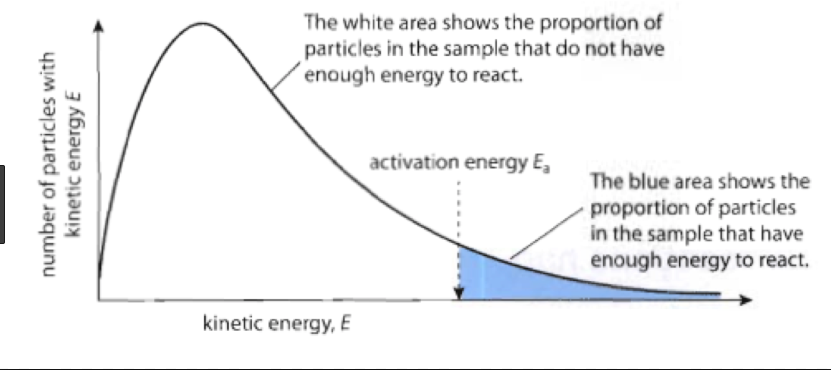
1. Construct a Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curve to account for the probability of successful collisions and factors that affect them, including the effect of a catalyst.
The Maxwell-Boltzmann graph is a distribution curve that shows the distribution of particles in a reaction. Below is a picture from chemguide.edu and a quick YouTube video summary. Study.com has a nice, extensive explanation that will help you answer the questions on the sheet.
Copy and paste this link to listen and/or read: http://study.com/academy/lesson/the-boltzmann-distribution-temperature-and-kinetic-energy-of-gases.html
Below image courtesy of getrevising.co.uk
Mission 3: Dudes Named Max and Bolt (sort of)...
Mission Objectives. You should be able to...
1. Construct a Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curve to account for the probability of successful collisions and factors that affect them, including the effect of a catalyst.
The Maxwell-Boltzmann graph is a distribution curve that shows the distribution of particles in a reaction. Below is a picture from chemguide.edu and a quick YouTube video summary. Study.com has a nice, extensive explanation that will help you answer the questions on the sheet.
Copy and paste this link to listen and/or read: http://study.com/academy/lesson/the-boltzmann-distribution-temperature-and-kinetic-energy-of-gases.html
Below image courtesy of getrevising.co.uk